Metabolomics and Natural Products Chemistry
Presentation
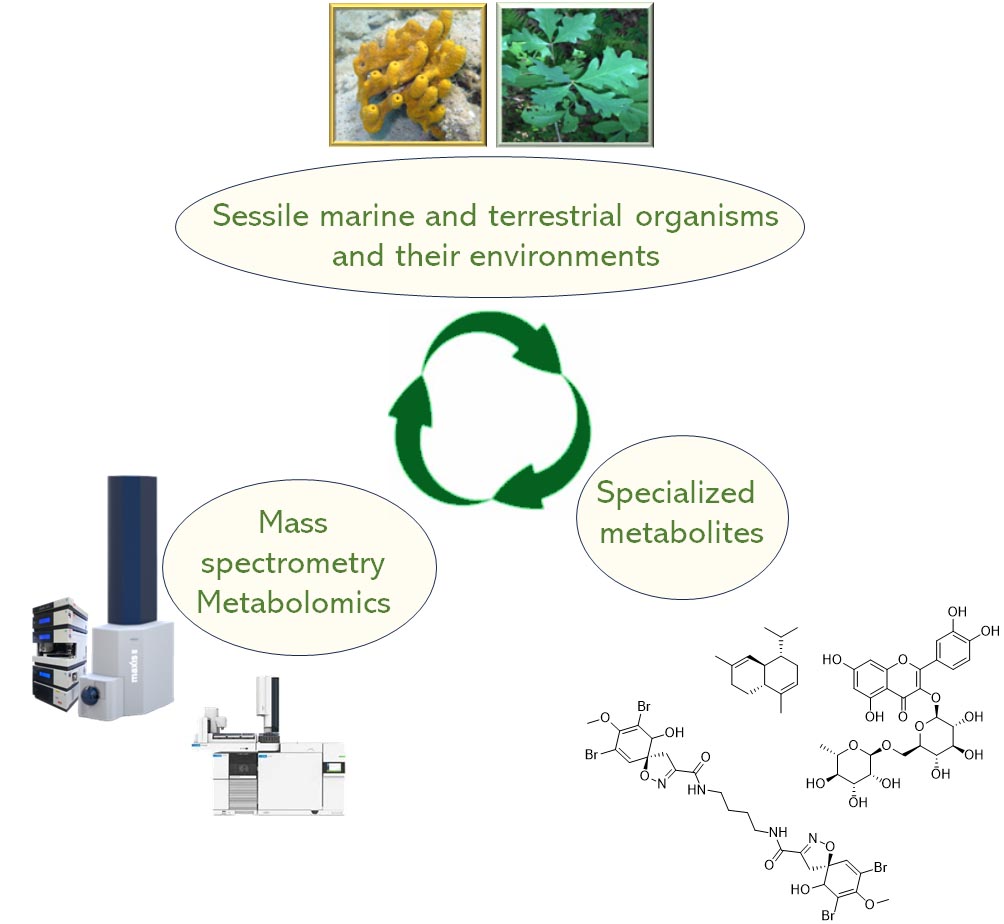
L'chemical ecology is a multidisciplinary field of research that studies interactions between organisms, as well as organism-environment interactions. These interactions are mediated mainly by specialised metabolites that play essential roles in the survival of an organism in its natural environment. They are the main mediators in chemical communication processes (pheromones, allelochemicals, volatile organic compounds) and thus make a significant contribution to the structuring of biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems. They also help to protect organisms from environmental stresses. The study of the biosynthesis and function of these molecules is therefore essential in the context of environmental issues, functional ecology and evolutionary ecology.
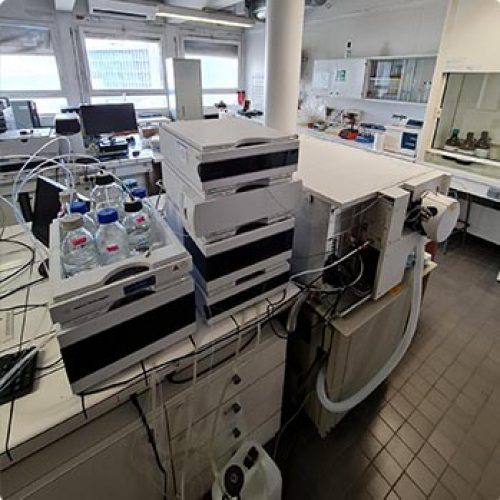
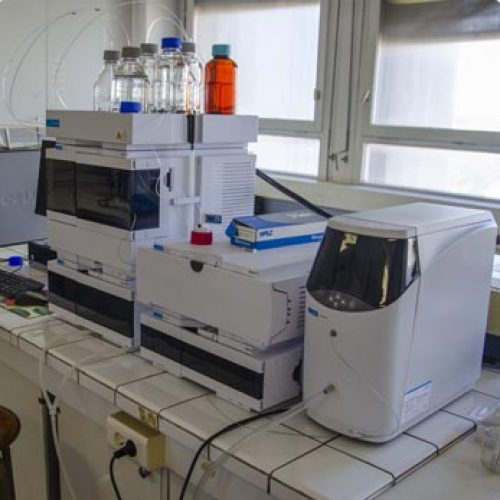
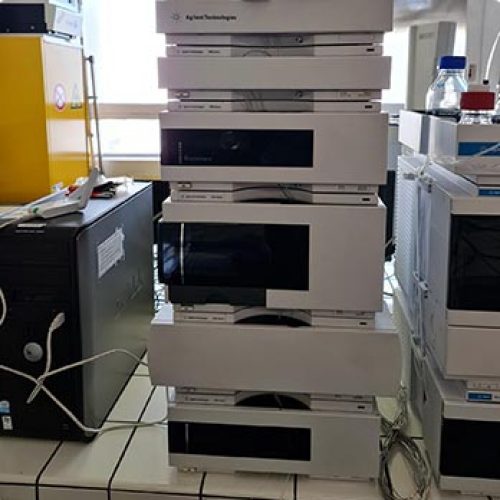
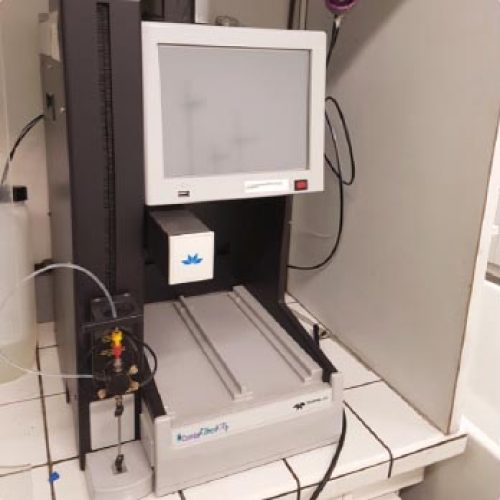
La metabolomics by mass spectrometry is an analysis method mainly used to understand qualitative and quantitative metabolic variations in organisms (marine and terrestrial), studied in particular in the context of global change.
La chemistry of natural substances associated with the purification and structural characterisation of metabolites reinforces the results of metabolomic analyses by confirming the structures of marker metabolites and offering the possibility of quantifying them in absolute terms in samples.
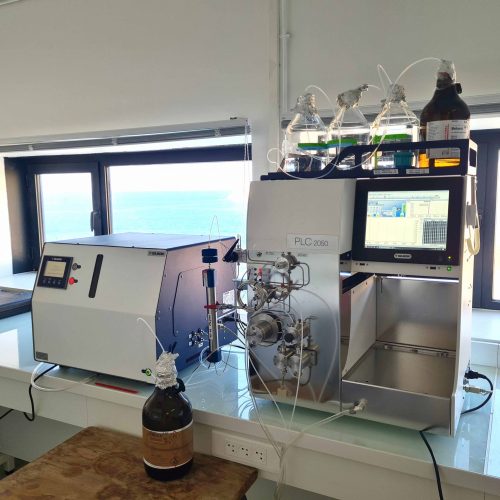
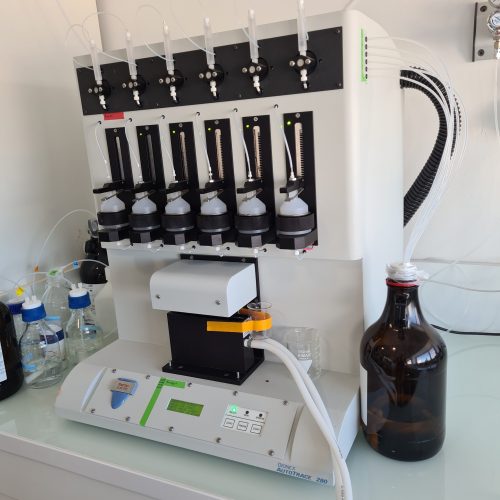
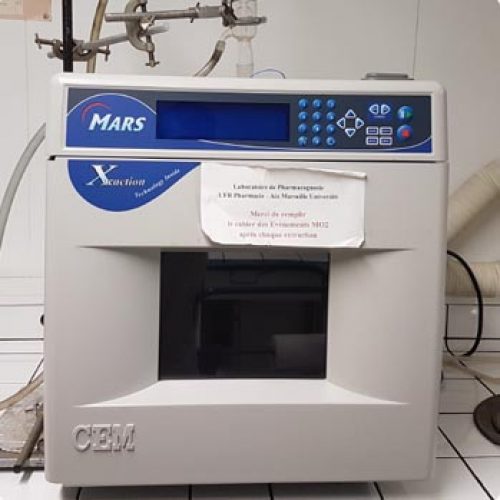
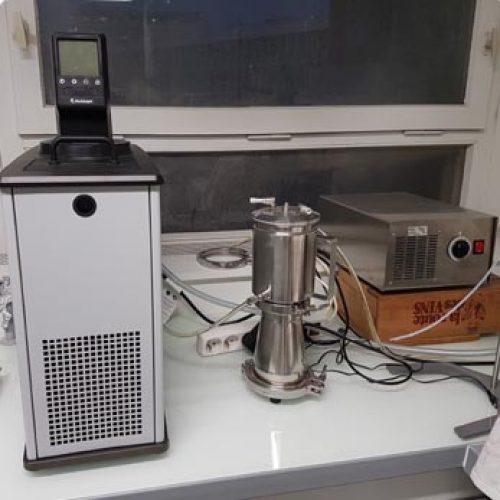
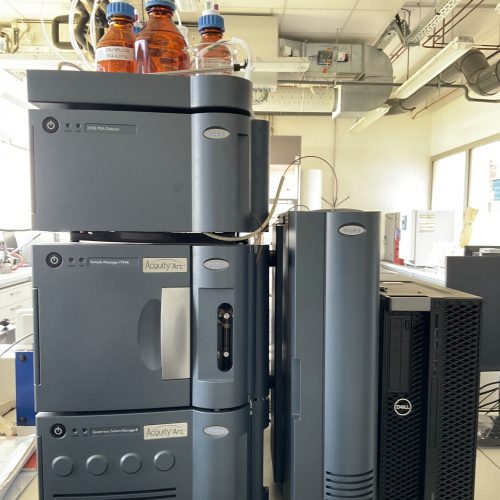
The Metabolomics and Chemistry of Natural Substances department brings together a range of complementary instruments distributed across 4 IMBE sites to carry out these analyses.
The contacts for each site are:
- Saint-Jerôme: Caroline Lecareux
- Endoume: Stéphane Greff
- Timone : Fathi Mabrouki
- Avignon: Céline Joliot
This joint service offers members of the unit :
- tools for preparing and conditioning samples prior to chemical analysis,
- methods for analysing organic compounds resulting from specialised metabolism,
- training in routine analysis methods and interpretation of results,
- Training in health and safety instructions for chemical analysis laboratories,
- support for the development and introduction of new methods