Cellular and molecular biology
Presentation
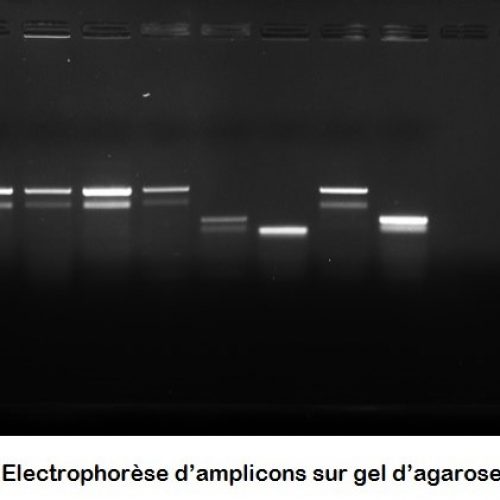
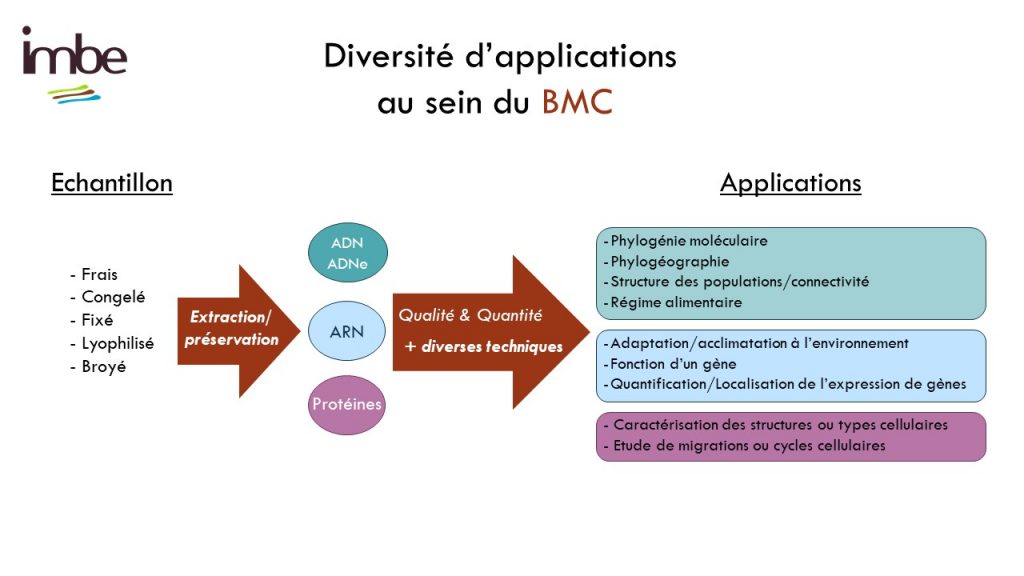
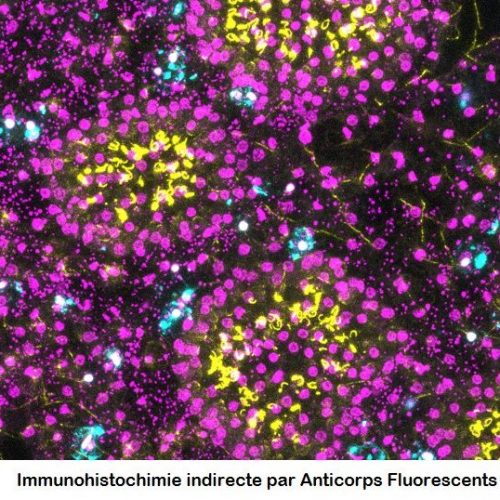
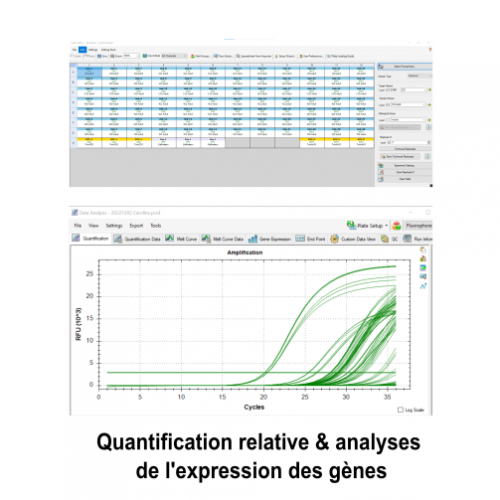
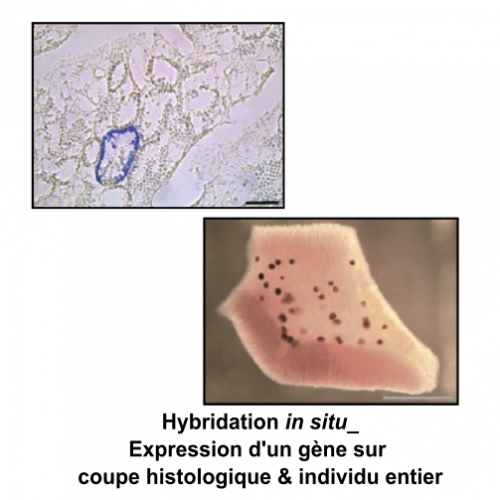
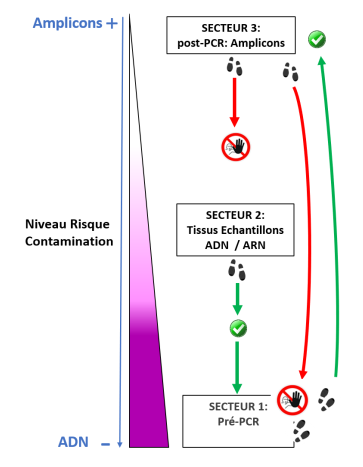
Le molecular and cellular biology department (BMC) is a technical platform located at the Endoume Marine Station, dedicated to the development of research projects focusing on the study of living macromolecules (DNA, RNA and proteins). It covers 250m2 of experimental laboratory space, with 15 shared rooms, each dedicated to a different type of experiment. In order to ensure a quality approach, a coherent 'one-way' circulation system (walking forward type) has also been put in place to limit the risks of sample contamination. This configuration is particularly advantageous for sensitive approaches such as metabarcoding.
The BMC's technical platform offers technical support services, training and advice to researchers and their teams, thanks to the support of the service team. In addition, the variety of shared equipment and consumables available enables the BMC to provide scientific leverage to tackle complex technical challenges while meeting the needs of the unit's thematic diversity. This includes the study of numerous unconventional biological models, whether marine or terrestrial, animal or plant.